Beam dynamics can be tracked by six variables:
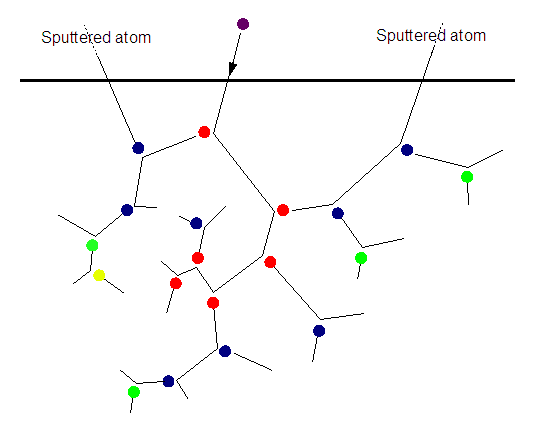
\[x, y, z, p_{x}, p_{y}, p_{z}\]The SNICS source produces a beam of heavy ions by way of sputtering. Cesium vapor flows into an enclosed chamber from an oven. Cesium atoms condense onto heated ionizers producing positively charged cesium ions. These ions are focused onto a target cathode capped by a condensed layer of cesium. The ions sputters particles through the cesium layer which favors the production of negative ions due to cesium’s low electron affinity. The negative ion beam is extracted and focused (electrostatic lenses?).
The alphatross source primarily provides \(H^{+}\) and \(He^{+}\) beams, but it is capable of providing a moderate beam current of light ion sources such as oxygen or chlorine. The positive ion sources are extracted from an RF plasma, driven by high frequency voltage.
“The charge exchange cell utilizes a rubidum vapor for its high cross section for He- production”
Like its namesake, the accelerator uses a pelletron charging chain made of metal pellets connected by nylon links to deliver current to high voltage terminals.

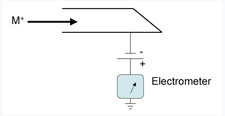
Faraday cups are charge particle detectors are typically used to tune ion beams. In the figure above, ions enters the Faraday cup, a current \(I\) is induced as ions neutralize on the metal cup. By measuring this charge \(I\), the number of charges carried by the ions in vaccuum can be calculated as:
\[\frac{N}{t} = \frac{I}{e}\]